What is Due Diligence in Project Finance Modeling
What Is Due Diligence in Project Finance Modeling? Key Roles & Process
Introduction: The Importance of Due Diligence in Project Finance
Financing decisions where risks and responsibilities are enormous in the world of large-scale infrastructure, renewable energy, and industrial projects are in the limelight. Lenders, investors, and sponsors have to consider not only financial potential of a project but also technical and legal as well as regulatory basis on which the success of the endeavour is based.
Here due diligence takes centre stage. The vice president of corporate finance was right when he stated that due diligence is not a check list on project finance modeling since it is an inclusive process through which the financial structure is based on the proper assumptions, the realistic projections, and the substantiated risk analyses. With inadequate due diligence, the most advanced model of project financing can distort risk levels, resulting in damaging distortions.
Understanding Due Diligence in Project Finance
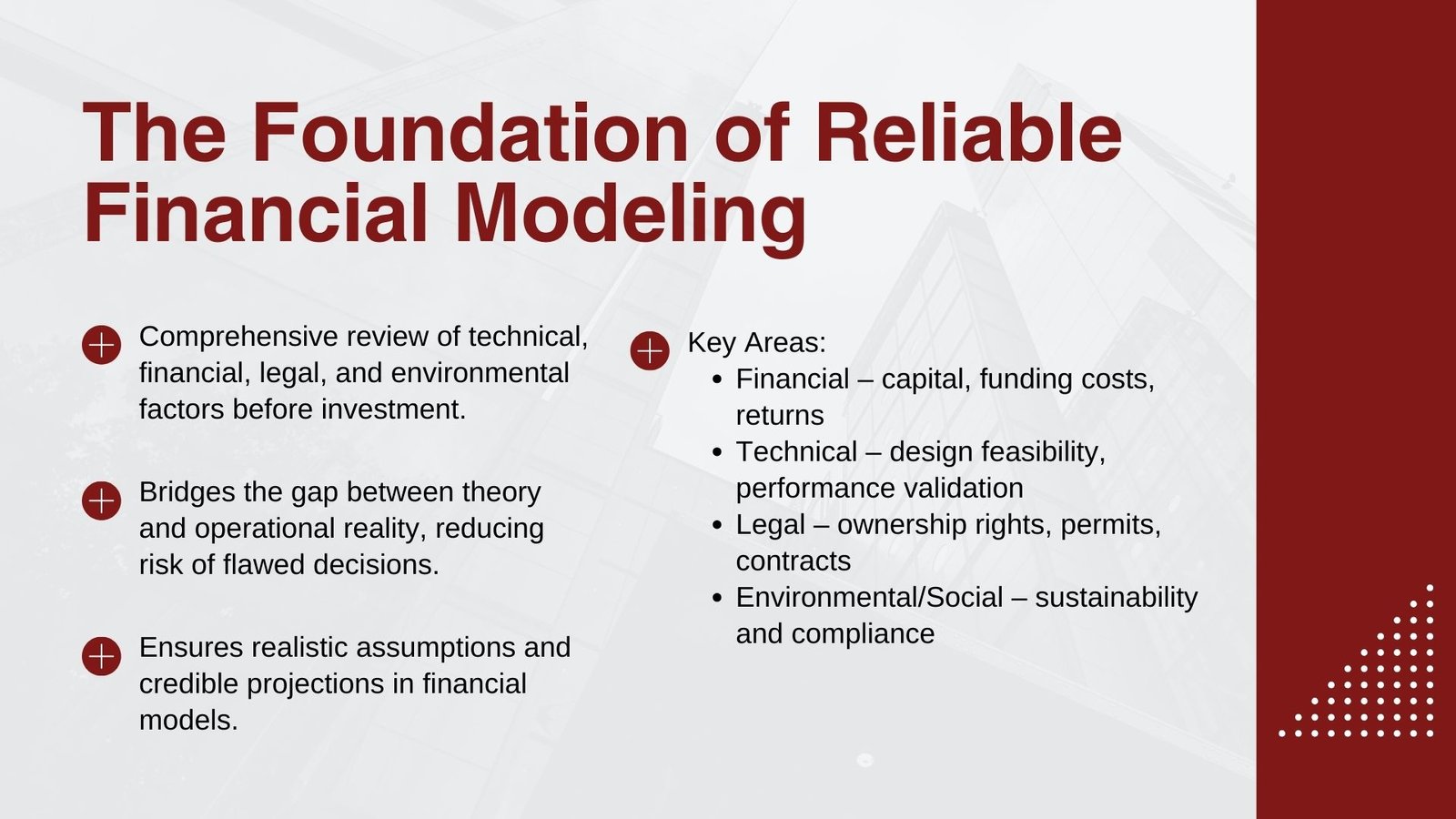
Due diligence in project finance All duty is the timely and orderly examining of all project details before the decision to invest further is made. It encompasses the validation of assumptions in the project, it determines the risks, and it checks its compliance with the law and regulations, as well as environmental frameworks. Regarding the financial model, due diligence tests inputs which go to the model, procedures used in testing forecasts and in continuity of cash flow predictions to financial realities.
The due diligence process is what puts together the gap that exists between financial theory and the reality of operations to the investor and the lender. It validates revenue sources, operating expenses that are not so unrealistic and financial obligations that are sustainable, turning a financial model into a credible decision-making instrument. For those seeking practical application, programs such as Due diligence training for finance professionals Singapore provide deeper insights into how these processes work in real-world scenarios.
Due diligence is defined in more than a few dimensions. Financial due diligence considers capitalisation, funding rate and returns. Technical due diligence is used to evaluate design, feasibility of construction and efficiency. Legal due diligence is concerned with ownership rights, regulation approvals and contracts. Environmental and social due diligence imply observing the requirements of sustainability and addressing the influence on the local population. All these areas combined will make sure that the financial model is not a standalone spreadsheet but the complete picture of the project reality.
The Key Roles in Due Diligence
The due diligence process under project finance is comprehensive and requires expertise of many different professionals that have a set of combination of skills. The most central role is played by financial advisors and analysts who develop, stress-test the financial model, and then validate it. It is their responsibility that the model correlates with the market situations, financing arrangements and project-level risks. Technical specialists, commonly engineers or specialists in the industry, make crucial inputs concerning the specifications of designing, the construction time frames and the performance points at which operations should take place. The assumptions in the financial model regarding costs, capacity and efficiency of the model would not be conclusive without their validation.
Legal representatives are just as vital to due diligence. They are subject to contracts in form of, but not limited to, power purchase agreements, concession agreements, loan covenants and regulatory permits. This is because their work makes all contractual demands coupled with the enforceability of the financial assumptions embedded in the model. There are also environmental and social experts that will ensure that the project is in compliance with international standards, regulations on the environment and green commitments. In the case of projects funded by international lenders, adherence to initiatives like Equator Principles or Performance Standards of the IFC, may be decisive in gaining approval.
One should not underestimate the role of lenders and investors. They will trust due diligence in justifying the investment actions but also participate directly in the process by outsourcing reviews and insisting that they carry out assigned stress activities. The development of the project should always be coordinated between all parties with the involvement of sponsors who initiate the project and whose interest is aligned. Finally, due diligence is a team exercise, which suggests a combination of various forms of expertise to create a financial model that is reliable in terms of accuracy.

The Due Diligence Process in Project Finance Modeling
The due diligence process in the project finance normally commences with information collection. Business plans, feasibility studies, technical designs and draft contracts are given by sponsors. Financial planners can then incorporate such inputs into a primitive financial model. This initial architecture is used to build upon and it enables the stakeholders to realise major assumptions that need to be ascertained. Such as, long-term power purchase arrangements revenue projections need to cross-check the contract terms as well as the market benchmarks.
It is after the step of information gathering that validation is done. All elements of the financial model are tested. Technical due diligence provides an assurance that the capacity factor or construction schedules projects correspond to engineering analysis. The financial due diligence confirms the availability of funding, cost of capital projections and debt repayment. Legal due diligence will ensure there is a legal agreement that backs the financial projections. During this readjustment, all the discrepancies are identified and corrections are taken to align the model with indisputable data.
Due diligence includes the risk assessment. Financial models also include sensitivity check and scenario testing which are used to quantify the effects of changes in the variables in terms of cash flows and debt service coverage ratios. To illustrate, the tardiness in the construction process and reduction in price in the market will have to be subjected to a test factor to gauge the strength of the financial model of the project under unfavorable conditions. These stress tests tend to be required by lenders and investors prior to funds being lent. The outcomes of these analyses are decisive when it comes to determining terms of loans, the amount of equity and the distribution of risk among the stakeholders.
It will end up with the creation of due diligence reports. Independent advisors give their observations, indicating the risks, assumption accuracy and recommendation. Such reports serve as the infrastructure of the last negotiations of the sponsors, lenders and investors. When milestone due diligence is accomplished and the financial model demonstrates validated inputs, stakeholders will be able to proceed with confidence that the project is on sound analytical and contractual footing.
Challenges and Limitations of Due Diligence
As necessary as due diligence is, it is not without its problems. Availability and quality of information are also one of such limitations. Projects at the initial stages could have less or even zero data, which means a project would require some assumptions due to which project could provide uncertainty in the financial model. The fast changing conditions in a market means that forecasts are less reliable. As an example, assumptions used at the time of due diligence might be distorted by a sudden upward swing of commodity prices or change in regulatory policy.
One more issue is the costliness and sophistication of the process. Sophisticated due diligence entails the use of more than one expert, independent advisers, and more intensive, extensive legal scrutiny, and it is costly and time consuming. The small projects might have difficulty in striking a balance between the requirement of good analysis and budgetary control. Also, due diligence is not objective. Risks can be perceived differently by different advisors and therefore they come up with different advice which the sponsors and the lenders have to iron out.
Such challenges notwithstanding, the restrictions of due diligence glorify its need as opposed to detracting its worth. Due diligence pays off because although no process can eradicate all risks, it assigns and quantifies the risk bearing. It also restructures uncertainty to manageable variables and the stakeholders can make decisions based on the available information.

Conclusion: Why Due Diligence Matters in Project Finance
Project finance modeling due diligence is far more than a checklist or even a verification operation; it is the basis of financial credibility and long term investment confidence. Throughout the systematic process of assumption validation, stress testing, and analysis of risks, due diligence confirms that financial models are not based on idealistic tendencies but on reality.
In addition to figures, it integrates multi-disciplinary knowledge of law, technical, operational and financial to develop models that can withstand the examination of various stakeholders. To the sponsors, it translates to negotiating with more credibility; to the lenders, it comes with the guarantee of knowing that the repayment schedules are untenable; and to the investors, it comes with the assurance that the projected returns are not pegged on speculation but rather on sound fundamentals.
The importance of due diligence could not be overemphasized as project financing remains the foundation of large-scale infrastructural, energy transition and renewable energy projects all over the world. Such ventures are typically high-risk and require complicated structures, extended timelines, and lots of capital. Unless due diligence is well done, these projects could be unbankable or they may not find credible funds. What due diligence does is to transform what can be considered inherently risky ventures into planned opportunities with visible cash flows, risk allocation, and mitigation strategies. This is one reason why financial institutions, development banks and private equity investors always insist on a strong due diligence as a non-negotiable part of any project financing process.
Lastly, due diligence in project finance modeling is not a number game or a beautiful spreadsheet game, it is a question of faith and doubt. It makes the expectations of each party consistent, so that assumptions are clear, risks are known, and financial forecasts can withstand reality tests.
This is so as to release the funds to fund the projects that would be on the drawing board to the reality such as renewable energy parks, construction and development of transportation infrastructure and social development projects can be pulled off the drawing board to the reality. By so doing, due diligence is fundamental in closing the gap between a visionary thought process and a sustainable financial implementation process and this means that it is a necessary component of successful project development.