Stress Testing and Scenario Planning in Project Finance Models
Stress Testing and Scenario Planning in Project Finance Models
Introduction to Stress Testing and Scenario Planning in Project Finance Models
Project finance models have been constructed to inform long-term investment decisions in large scale infrastructure projects as well as energy and industrial projects. These models predict cash flows, financing requirements, and returns over decades; however, there is never a perfect forecast. Outcomes can be greatly changed by the volatility and delays of the market, alterations in policies. It is at this point that stress testing and scenario planning come into play, that is, to assist analysts and stakeholders to find out how a project can withstand uncertainty. Professionals who attend project finance modeling training Singapore often learn how to effectively apply these techniques to build resilient and realistic financial models.
Project finance professionals are able to predict the risks that will arise by modeling various financial and operational conditions. This is not aimed at foreseeing the future but to be ready.
Risk Assessment is of Importance in Project Finance.
When it comes to project finance, the model should be successful in replicating complexities relating to the real-world. The projects are usually associated with a lot of debt and long-payback periods, which imply that minor changes in major assumptions can have significant effects.
As an illustration, a sudden increase in the interest rates will result in a decrease in the cash flows that can be used to service debt and any delays in the construction process will force the generation of revenue to be further in the future. Unless they are designed with operational flexibility and vision, these aspects may result in breach of covenant or liquidity challenges.
These potential risks can be seen by decision-makers by using stress testing and scenario planning. These assist the lenders in determining how well a project can respond to downside shocks and still fulfill its obligations. These tools are used by investors in deciding whether the equity returns are worth the risks. Regulators and sponsors, in their turn, can have a better understanding about the overall soundness of the project.
Stress Testing Explained.
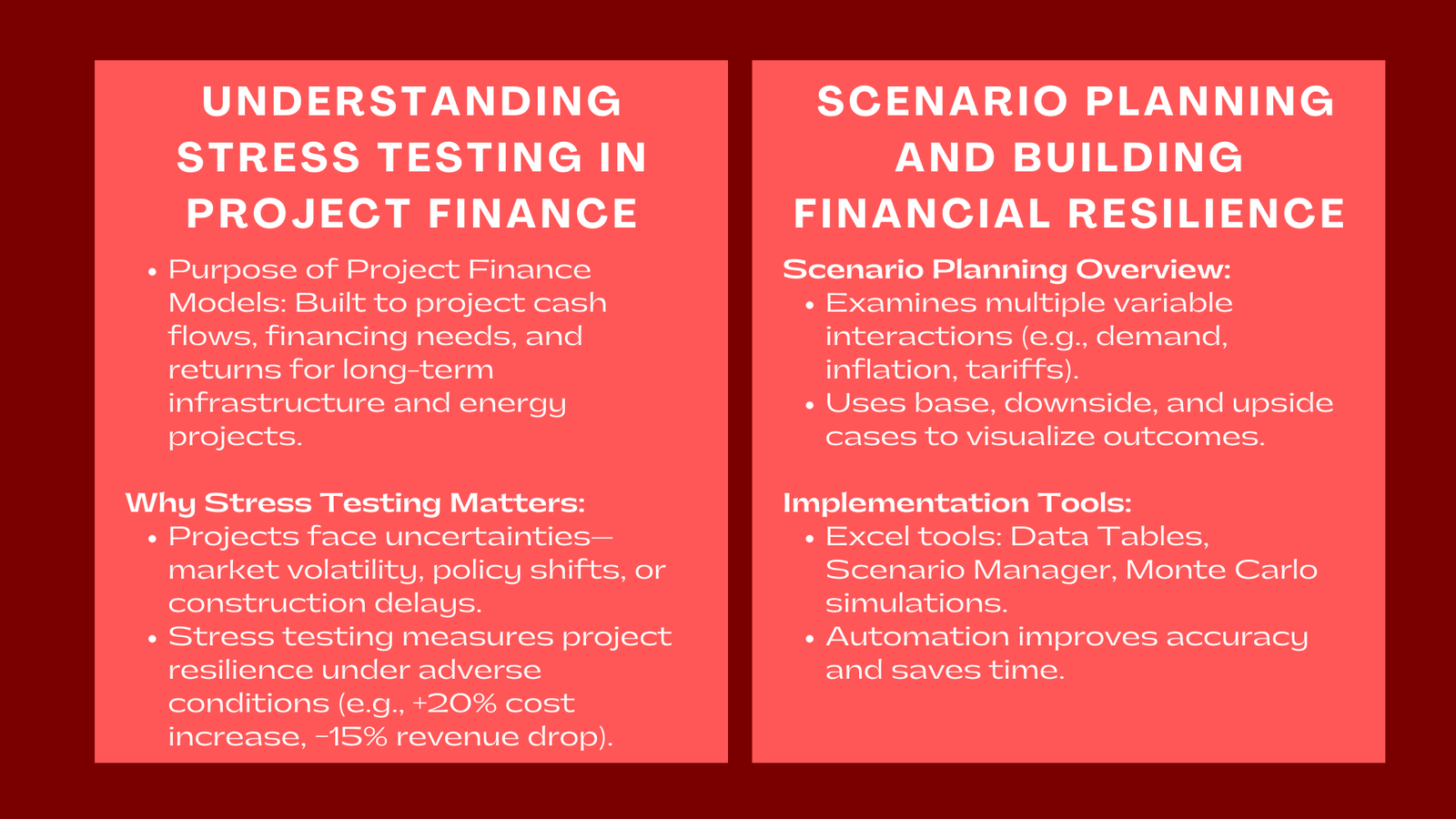
Stress testing looks at the impact of abnormal events of financial performance but which are plausible. In a project finance model this entails the manipulation of critical variables to model what-if conditions.
As an illustration, the sensitivity of the model to a 20 percent rise in building expenditures or an unexpected decline in the revenues by 15 percent as a result of falling demand can be tested by analysts. Such situations indicate the response of major indicators (the Internal Rate of Return (IRR), Net Present Value (NPV ), and the Debt Service Coverage Ratio (DSCR) to exogenous shocks.
Stress tests results assist in the determination of financial buffer of the project. When a project has the capability to have a minimum DSCR given stressed conditions, it could be said to be financially resilient. Otherwise, the sponsors may think about modifying the capital structure, renegotiating the terms of debts or adopting hedging measures.
Financial models are also made more credible through stress testing. Until lenders are satisfied with the outcome of stress tests, they often insist on having detailed results because it will help them to ascertain that the model has undergone a careful test against uncertainty.
Scenario Planning: Wider Perspective.
Whereas stress testing is concerned with individual or extreme variables, scenario planning is a wider perspective. It analyses the interaction of various variables given varied market or operational conditions.
An example of a base case scenario can be expected performance and a downside scenario may cover slower growth in demand, increased inflation and late commissioning. On the other hand, a positive situation may involve pleasant market conditions and quicker than hoped acceleration.
Scenario planning is used to assist the analysts to visualize the project financial results in the event of different economic realities. It also aids in strategic decision making i.e. identifying whether to go on with the construction or to pursue alternative finance or to renegotiate supply contracts.
Scenario planning in project finance is a way of thinking in advance as opposed to having to react. It provides an assurance that both sponsors and lenders know the full gamut of possible results and make financial commitments.
Introduction of the Scenario Analysis in Models.
Efficient scenario planning must have well-modeled dynamic financial models. The inputs should be adaptable such that the analyst has the ability to change several assumptions at a time.
More typically switches or dropdowns are used in practice to alternate between preset cases, e.g. base, upside and downside. In both cases, there are a set of assumptions of the key drivers such as capital cost, tariffs, inflation and operating efficiency.
The process is further increased with automation. Excel provides analysts with rapid access to evaluating the financial implications of various variables using the functions of data table and scenario manager. This is flexible and saves time, and it is also consistent when reporting the results to lenders or investors.
In case of long-term infrastructure projects, the scenario analysis with probability-based methods including Monte Carlo simulations can further reveal information. It is a measure of the probability of some outcomes, which can assist teams in determining the most attention should be paid to the risks.
Real-World Project Finance.
Scenario planning and stress testing are not notions of theory, they are vital elements of decision-making in the real world. As an example, cash flows in the renewable energy projects are sensitive to generation capacity and market prices. As a way of forecasting the impacts of an unfavorable environment on debt repayment cycles, an analyst can test how the changes in the energy production or tariff rates would influence the debt repayment rates.
And likewise, the transport and toll road projects are subject to unpredictability in the volume of traffic and cost of operation. Through several traffic demand scenarios, investors will be able to determine the viability of the project in case the actual usage is lower than what is projected.
These analyses are normally used by banks and other investors to decide on the terms of financing. The resilience of projects in various situations will increase their chances of getting funding at good rates. On the other hand, when stress tests indicate weakness, stakeholders might require to make extra contribution of either equity or reserve accounts to mitigate risk exposure.
The Purpose of Advanced Modeling Tools.
Although Excel is the standard in the industry, there has been the emergence of specialized project finance modeling platforms and training programs in order to increase the accuracy of the analysis. Professionals seeking to deepen their technical expertise often enroll in project finance risk modeling and sensitivity analysis courses that teach how to integrate stress tests and scenario logic effectively.
This kind of programs focuses on transparency, disciplined structure and repeatability – features that enhance a strong model to that of a spreadsheet. They also bring in automation methods that enable complex analysis to be done in a faster and reliable way.
The next aspect of focus is better documentation and model auditability. A documented model will help in making sure that every stakeholder, including the junior analysts and the senior lenders, will be able to follow the assumptions and the manner in which the results are to be obtained. This is essential in ensuring that one has a sense of confidence in financial findings based on stress and scenario analysis.
Developing a Financial Resilience Culture.
Scenario planning and stress testing work best when inculcated into a larger risk management culture. Organizations that constantly refresh assumptions, track project performance and re-run scenarios can keep up with the emerging threats.
Financial teams that undergo specialized infrastructure finance modeling and scenario planning training gain a deeper appreciation for how to translate uncertainty into actionable insights. They are taught how to take variability as an aspect to be controlled rather than to be afraid of.
By integrating the practices into the organizational workflow, it is possible to make sure that the decisions are made on the basis of the quantitative evidence instead of intuition. This field helps to enhance the credibility of the institution among the lenders, investors and regulators in the long run.
Conclusion
No model can be used in predicting the future in project finance with absolute accuracy. Nevertheless, systematic stress tests and scenario plans allow financial professionals to comprehend the variety of potential consequences and to be ready to them. These tools make uncertainty into strategy – enabling teams to protect investments, stay afloat and make decisions that are more informed.
Perfect forecasting is not the real worth of project finance modeling but resilient planning. The stress test and scenario analysis guarantee that despite the fluctuating conditions, the projects do not become unsustainable financially and in terms of strategy.